CD96 is classified among the immune checkpoints governing NK cells, representing an innovative focal point for cancer immunotherapy. It has been revealed to modulate the efficacy of NK cell functions and the metastatic process. CD96 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), which was initially unveiled during the 1980s. The prevailing portion of IgSF entities predominantly constitutes transmembrane glycoproteins, fulfilling roles as cellular adhesion molecules. In the case of the hCD96 subtype1, its domain configuration encompasses V, V, and C segments; meanwhile, for both the hCD96 subtype2 and mCD96, the domains consist of V, I/C, and C components.
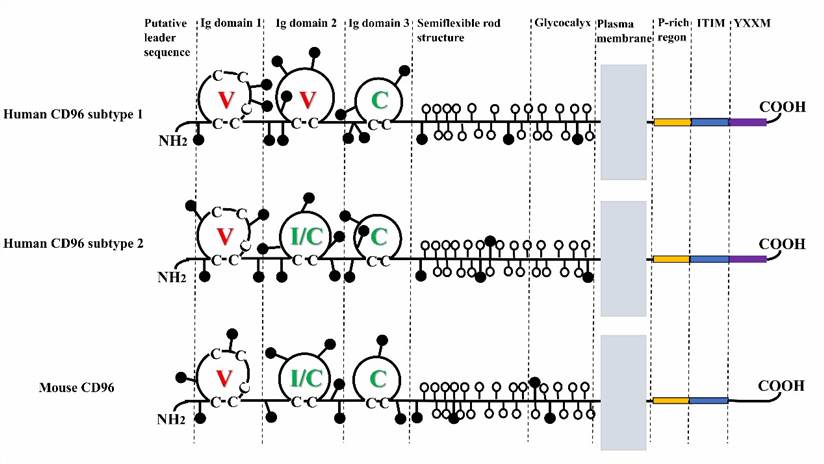 Fig.1. Structure of CD96 molecule.1,2
Fig.1. Structure of CD96 molecule.1,2
The TIGIT and CD96 pathway alongside CD226 (DNAM-1) resembles the CD28/CTLA-4 Pathway. Analogous to CD28 and CTLA-4, CD226 acts as a co-stimulatory receptor, sharing ligands with TIGIT and CD96, which function as co-inhibitory receptors. CD226 and TIGIT interact with two nectin and nectin-like (necl) proteins: CD155 (PVR, necl-5) and CD112 (PVRL2, nectin2). CD96 shares CD155 binding with CD226 and TIGIT, while also engaging with CD111. The interaction between CD96 and CD155 facilitates cell-cell adhesion, as observed in CD96-expressing engineered cells, NK-cell lines, and both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. An anti-CD96 monoclonal antibody that obstructs CD155 interaction could diminish trans-endothelial migration but not chemokine-mediated transmigration.
Findings in this research indicated that anti-CD96 augmented the effectiveness of various immune checkpoint inhibitors against tumors. The synergistic mechanism of combining anti-CD96 with anti-TIGIT hinged on CD8+ T cells, while having no reliance on NK cells.
CD96 emerges as a promising immunotherapeutic candidate, potentially augmenting existing glioma immunotherapy approaches. CD96 exhibited strong correlations with TIM-3, PD-L1, CTLA-4, and STAT3, implying potential synergistic interactions between CD96 and these checkpoint constituents.
Creative Biolabs stands as a proficient facilitator in the realm of immune checkpoint drug development, with over a decade of dedicated expertise in this domain. We possess extensive proficiency in delivering an array of tailored services related to the CD96 immune checkpoint molecule, encompassing an array of offerings, including but not restricted to: biomarker development for immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), immune checkpoint assays, preclinical research for immune checkpoint targeting drugs, etc. For those intrigued by our services, please don't hesitate to contact us for additional details.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.