Nowadays, costimulatory pathways play an important role in mediating immune responses against infections and treating various human diseases. Up to date, a wide range of immune checkpoint molecules, such as 4-1BB, GITR, OX40, and CD28, have been considered as key components of co-stimulatory pathways regulation. These co-stimulatory molecules and their receptors can activate immune cells, like T cells, to trigger strong immune responses to pathogens. Immune checkpoints have been classified into two main costimulatory molecules, the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily costimulatory molecules and the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily costimulatory molecules. For instance, CD28/B7-1 is one of the common costimulatory pathways of the Ig family. CD28 can be expressed on T cells and enhance the interaction between T-cells and antigen-presentation cells (APCs) and strengthen the proinflammatory signals. OX40/OX40L is a typical costimulatory pathway of the TNF family. The OX40/OX40L axis can enhance the survival of T cells, B-cell differentiation, and trigger cytokine production.
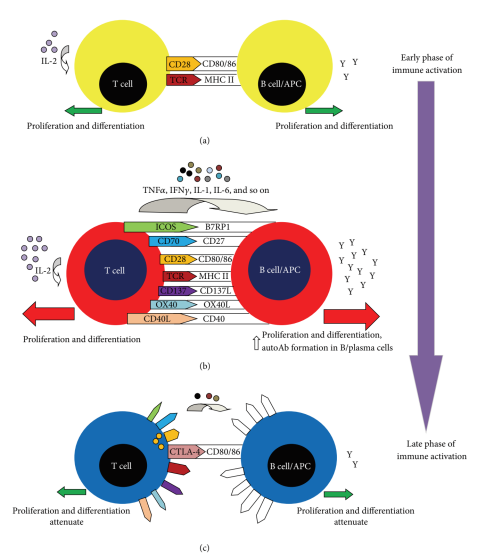 Fig.1 Intracellular Signaling Pathways of Costimulatory Molecules. (Kow, 2013)
Fig.1 Intracellular Signaling Pathways of Costimulatory Molecules. (Kow, 2013)
The costimulatory pathway initiates and maintains pro-inflammatory processes by maintaining homologous interactions between activated T cells and APCs, which are key to pathogenicity. Meanwhile, many reports have shown that the costimulatory pathway can attenuate subsequent uncontrolled inflammatory responses. Therefore, a large number of organizations and companies are dedicated to developing costimulatory drugs of different immune checkpoints. For example, different immune checkpoint molecules have shown distinct signaling mechanisms to inhibit antitumor immunity. In this condition, co-stimulatory pathways have been regarded as potential therapeutic targets for drug development.
Till now, a wide range of criteria protocols for novel drug discovery targeting multiplex co-stimulatory pathways has been developed. Equipped with big immune checkpoint databases, they have also established some immune checkpoint assays for detecting the binding and interaction of co-stimulatory molecules. Also, the efficacy and safety of costimulatory blockades, such as using antibodies and small-molecule drugs, have been broadly evaluated in various disease models. Currently, a series of co-stimulatory pathways targeting different immune checkpoint molecules have been characterized for drug development, including but not limited to:
Through our comprehensive early drug discovery services, Creative Biolabs is committed to developing the most promising co-stimulatory-based drugs for our clients. We will help our worldwide customers reduce drug discovery time and bring new drugs into the market for a wide range of disease treatments. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.