VISTA is a member of the B7 family that represents a new target for immunotherapy. Murine VISTA is a type I transmembrane protein with a single IgV domain that shares sequence homology to its B7 relatives with conserved segments thought to be critical for the IgV stability. The preclinical studies on multiple murine models showed that VISTA blockade improved the infiltration, proliferation, and effector function of tumor-infiltrating T cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME), thus altered the suppressive character of the TME. Based on the newest study, VISTA was regarded as a promising target for patients with cancers.
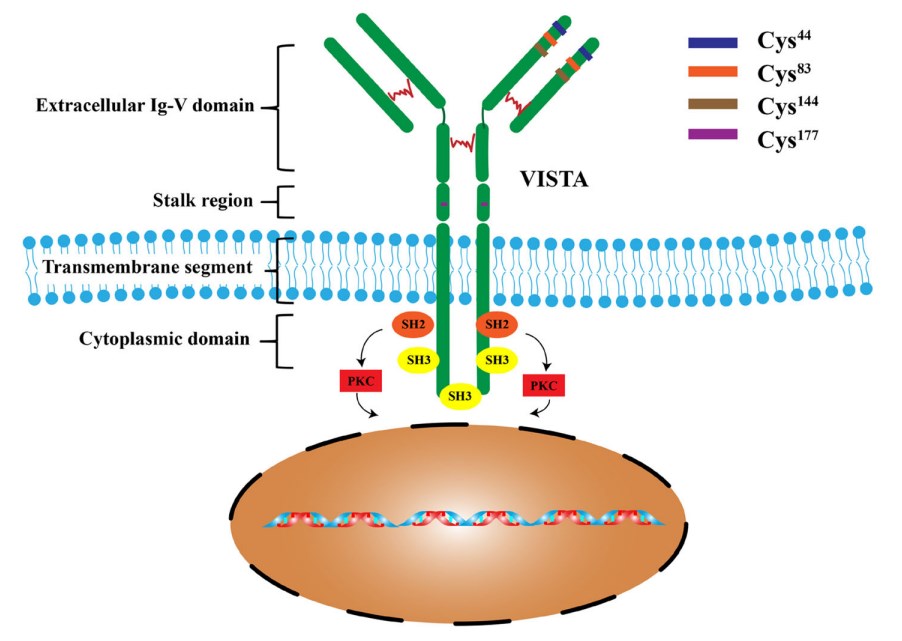 Fig.1. VISTA structure and its downstream signaling.1,3
Fig.1. VISTA structure and its downstream signaling.1,3
Scientists have demonstrated that VISTA is highly expressed and plays an immunomodulatory role in human NSCLC, suggesting that it may be a potential pivotal therapeutic target for the treatment of NSCLC.
A study shows that an anti-VISTA antibody extends the survival of tumor-bearing mice. The increased expression of VISTA is related to the advanced disease stage and lymph node metastasis (LNM), which means that VISTA is involved in ovarian cancer progression.
Scientists research the acute myeloid leukemia (AML) mouse model, and they found that the proliferation of leukemia cells was reduced in VISTA-knockout mice. When using VISTA-blocking antibody treatment in vivo, leukemia growth was further declined.
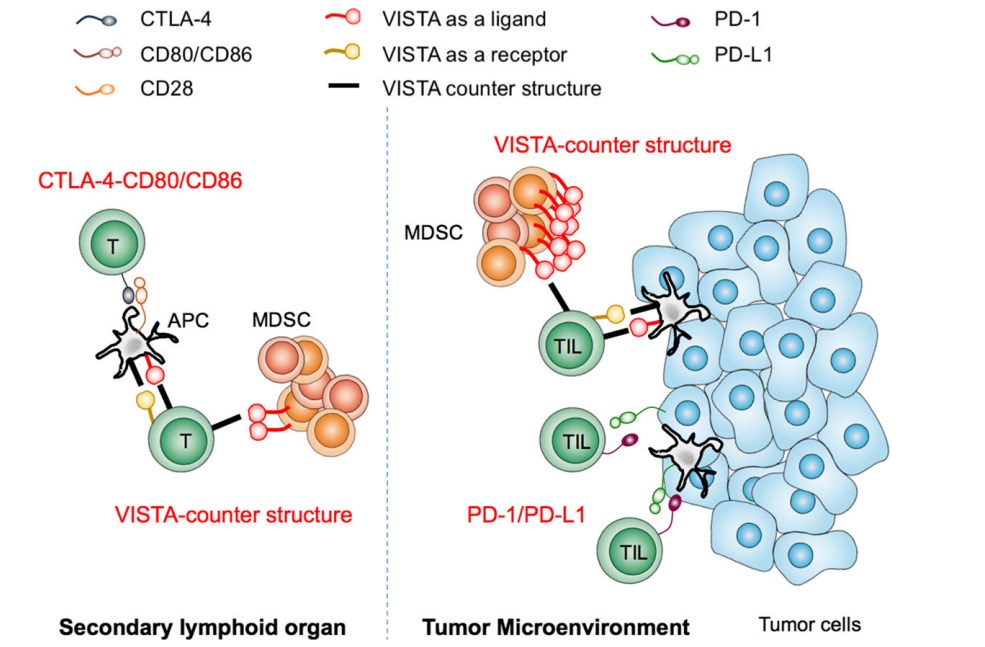 Fig.2. VISTA functions.2,3
Fig.2. VISTA functions.2,3
VISTA occupies a unique position as a candidate for cancer immunotherapy due to its expression pattern and activity. Firstly, VISTA expression on infiltrating myeloid cells is consistent across tumor types, making it relevant to a breadth of patients. Expression of VISTA is further enhanced by hypoxia and cancer progression. While most immunotherapy targets address either T cell or myeloid functions, VISTA has clear activity in regulating both arms. VISTA is also a promising target for combinatorial approaches to immunotherapy. Ideal combination therapy should address both myeloid and T cell responses. Releasing suppression by myeloid cells by targeting VISTA would improve T cell-focused therapies like anti-PD1 and anti-CTLA4.
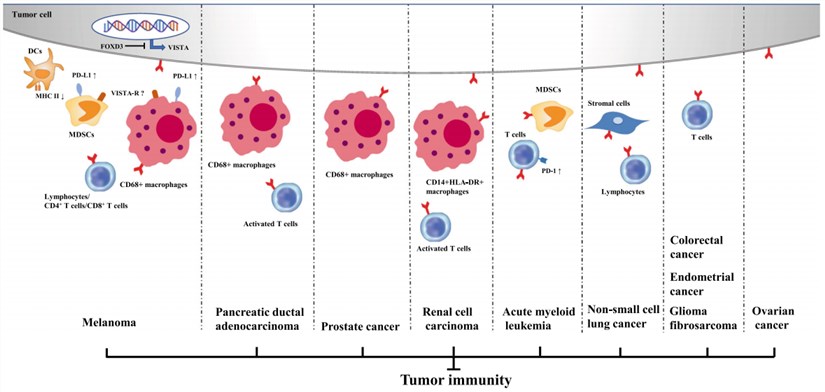 Fig.3 Inhibitory roles of VISTA in anti-cancer immunity. (Xing, 2020)
Fig.3 Inhibitory roles of VISTA in anti-cancer immunity. (Xing, 2020)
Our expertise in Creative Biolabs can provide flexible solutions for your choice; either a stand-alone service or integrated project is welcome to meet every specific demand. We offer the following immune checkpoint drug development services for worldwide customers.
For any questions, please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.