As a newly found member of the B7/CD28 superfamily, B7-H3 (CD276) is an accessory costimulatory molecule that belongs to type I transmembrane protein. Because B7-H3 is overexpressed in several kinds of human cancer cells and correlated with disease deterioration, B7-H3 has recently been identified as a promising candidate target in multiple cancers.
Increasing data suggest that inhibition of B7-H3 may suppress tumor growth, and B7-H3-targeted therapy has shown broad tumoricidal and antimetastatic activity in vivo. Human B7-H3-Ig fusion protein is found to increase the proliferation of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and enhance the cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activity in vitro, under the condition of an anti-CD3 antibody mimicking the TCR signal.
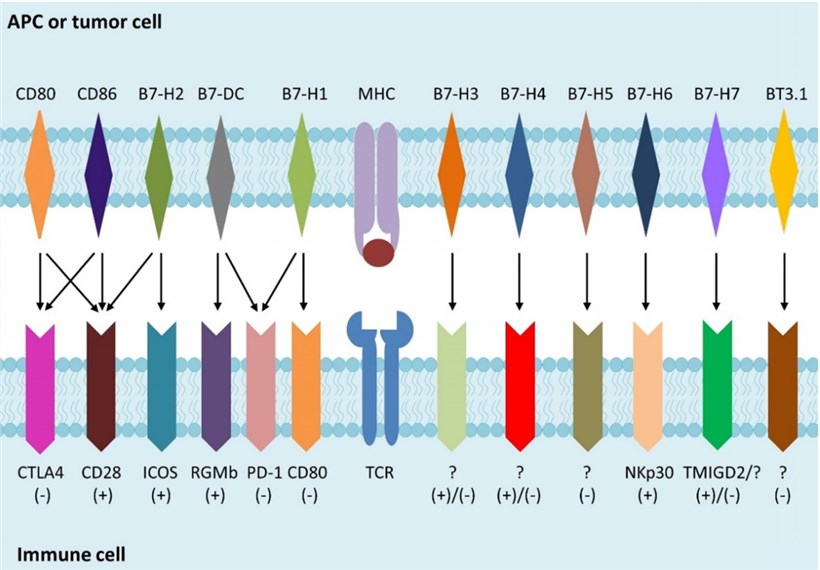 Fig.1. B7 family members and their receptors.1,3
Fig.1. B7 family members and their receptors.1,3
In a study, scientists constructed an orthotopic colon cancer mice model to study the mechanism of B7-H3 antitumor ability. The results revealed the antitumor effect of B7-H3 on colon adenocarcinoma, which could be regarded as a promising therapy for the treatment of colon cancers.
In another study, scientists demonstrated for the first time that downregulation of B7-H3 reduced cell adhesion to fibronectin by up to 50% and migration and invasion by more than 70% in melanoma and breast cancer cells. B7-H3 downregulation also led to significant inhibition of cell migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cells.
These results strongly suggest that B7-H3 is involved in cancer progression and metastasis beyond modulating tumor immunity.
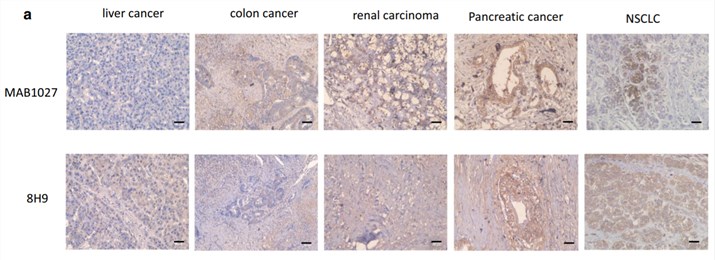 Fig.2. Expression of B7-H3 in human tissues.2,3
Fig.2. Expression of B7-H3 in human tissues.2,3
An anti-B7-H3 monoclonal antibody (mAb) shows to mediate potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against a broad range of tumor types. Anti-B7-H3 therapy has been studied in preclinical or clinical trials for treating refractory B7-H3-expressing tumors such as melanoma and B7-H3-expressing neoplasms, including osteosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma.
With many years of experience in immune checkpoint research, Creative Biolabs offers the highest quality services and flexible solutions quickly and cost-effectively. Our immune checkpoint development services cover Immune Checkpoint Protein, Immune Checkpoint Antibody, Immune Checkpoint Targeted Peptide, Immune Checkpoint Targeted Small Molecule Drug, Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) Biomarker, and Immune Checkpoint Assays.
For any questions, please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.