Checkpoints are some receptors expressed on the surface of cancer cells, which are used to evade the recognition of immune cells in the process of metastasis. Therefore, immune checkpoints and the immune system in the microenvironment play an important role in the prevention and control of tumor growth. Creative Biolabs will work with you at all stages of the immune checkpoint drug development process, from the initiation of your project to the final production.
CD47 is a transmembrane protein widely distributed on the surface of normal cells. It includes an N-terminal extracellular variable region, five hydrophobic transmembrane helices, and a very short C-terminal intracellular signal sequence.
CD47 plays an important role in the migration of endothelial cells. In a study, scientists found that the level of CD47 is positively correlated with the high invasion and metastasis ability of cancer cells. In non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLC), CD47 is expressed at a higher level. It means that these cancers easily escape immune cells to transfer to arrive lung.
A previous study showed that the stimulation of macrophages and NK cells could be promoted by blocking the CD47 signaling pathway of cancer cells. In another study, mice were injected with SIRPα-inhibited macrophages to block recognition of its ligand CD47. The results showed that this way could suppress tumors, just like that injected anti-CD47 antibodies could also be used to promote macrophages' activity and eliminate tumor cells. Today, exploring the inhibition of the SIRPα-CD47 pathway has been an approach to treating various cancers.
Scientists found that high expression of CD47 promoted the proliferation and invasion of GBM cells but did not affect the proliferation of normal astrocytes. However, another study draws a different conclusion that CD47 enhances the invasion of GBM cells through PI3K / Akt pathway but has no effect on cell proliferation. Some evidence shows the cytotoxicity of macrophages and neutrophils can be inhibited, and antigen presentation function of dendritic cells can be limited by CD47 SIRPα interaction.
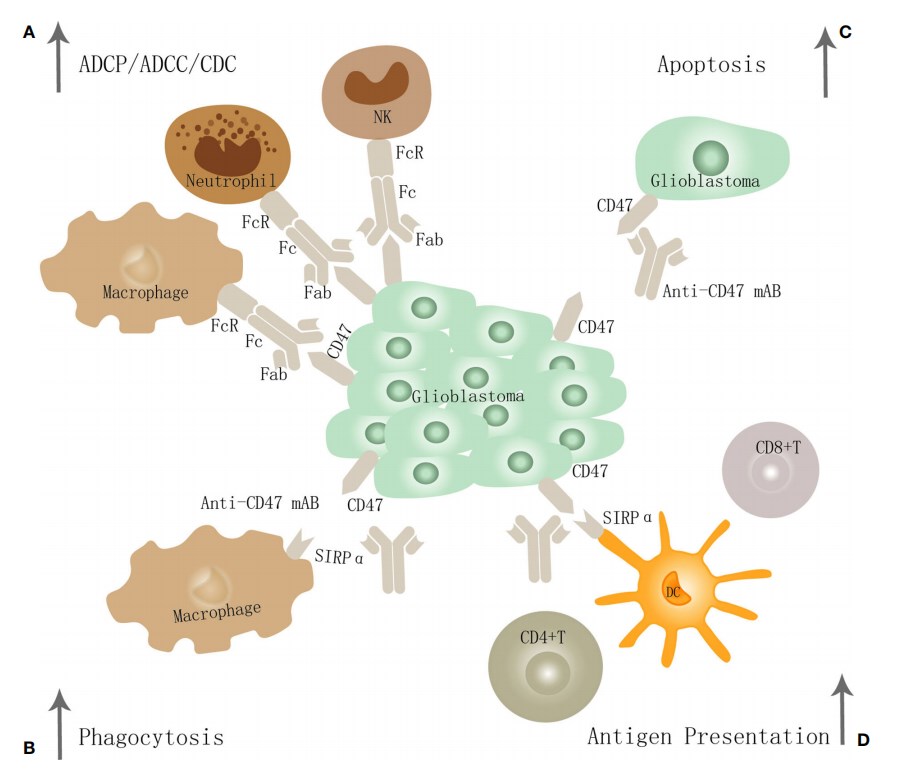 Fig.1. The potential mechanism of CD47-SIRPα inhibition in GBM.1,2
Fig.1. The potential mechanism of CD47-SIRPα inhibition in GBM.1,2
Creative Biolabs provides various drug development services based on the immune checkpoints, which includes but is not limited to: immune checkpoint antibody development, immune checkpoint targeted peptide development, immune checkpoint targeted small molecule drug development. If you want to know more information, please directly contact us.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.