At Creative Biolabs, we have accumulated extensive experience in immune checkpoint-related research, enabling us to provide comprehensive services for our clients. Here, we place a special focus on the CD70-CD27 signaling pathway, an attractive target based on immune checkpoints.
CD27 is a transmembrane phosphoglycoprotein expressed on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, providing co-stimulatory signals to T cells by inducing cell proliferation. As the only known ligand of CD27, CD70 is a strictly regulated type II transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 50 kDa, consisting of 193 amino acids.
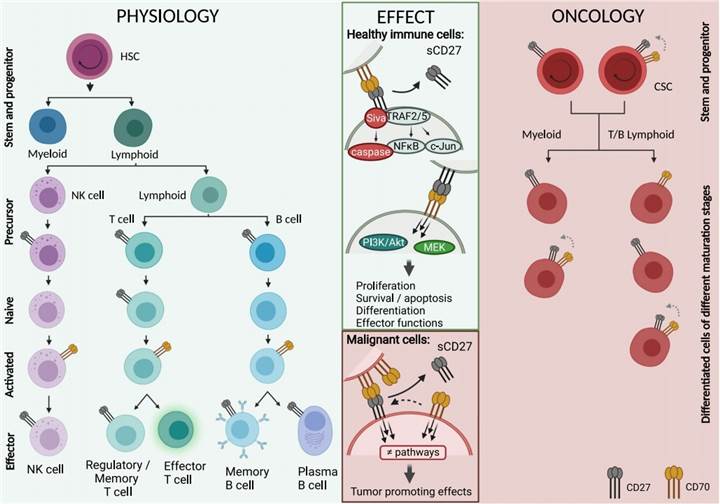 Fig.1. CD70-CD27 signaling pathway.1,2
Fig.1. CD70-CD27 signaling pathway.1,2
During normal hematopoietic development, the expression of CD70 is tightly regulated and limited to activated DCs, B cells, conventional/regulatory T cells, and NK cells. The activity of CD27-CD70 signaling is usually activated under pro-inflammatory conditions. Upon interaction with CD70, cytoplasmic residues of CD27 activate the NF-κB and c-Jun kinase pathways via TRAF2/5, leading to the initiation of various downstream effects:
Extensive research has validated the dysregulation of the CD70-CD27 axis in tumors, which is associated with tumor progression and immune suppression, exhibiting characteristics contrary to physiological conditions. For instance, abnormal CD70 expression has been observed in glioblastoma, melanoma, and lymphoma:
Tumor cells employ various mechanisms to evade detection and elimination by the host immune system, with the CD70-CD27 signaling pathway recognized as an important participant. Three important immune escape mechanisms involving CD70 have been confirmed:
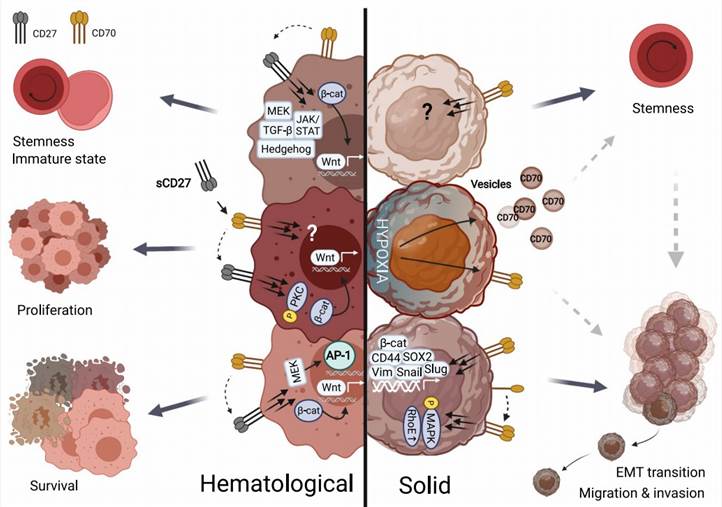 Fig.2. CD70 in tumor environment.1,2
Fig.2. CD70 in tumor environment.1,2
Due to the abundant expression of the CD70 immune checkpoint in various types of tumors, it has emerged as a promising target for novel tumor interventions. Current CD70 research pipelines primarily focus on phase I clinical trials and involve monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), CAR-T therapy, and combination therapies. The mainstream development strategies include:
Creative Biolabs' dedication to constant research and development enables us to stay at the forefront of the immune checkpoint field, pioneering new techniques and methodologies. This empowers us to offer groundbreaking solutions that not only address current challenges but also anticipate future trends. Our proven track record of success, coupled with our relentless pursuit of innovation, makes us the ideal choice for all your immune checkpoint-related needs.
At Creative Biolabs, we invite you to contact us today to collaborate with our team of experts and transform your research goals into reality.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.