BTLA (B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator), also known as CD272, is identified as an inhibitory receptor that is a member of the B7/CD28 superfamily. Ligation with its ligand HVEM (herpesvirus entry mediator, also called TNFRSR14, CD270) could block B cell and T cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. For more information on BTLA-involved pathways, please visit BTLA and HVEM pathway.
Table.1 Immune checkpoint BTLA.
| Checkpoint receptor | Alternate name | Cell type affected | Ligand | Function of ligand-receptor interaction | Notes |
| BTLA | CD272 | Naive T and B cells and further upregulated on the activation. |
HVEM (TNFRSR14 or CD270) |
Co-inhibition | Ligation of TNFSF14 by HVEM can be co-stimulatory, whereas BTLA-HVEM binding is considered co-inhibitory. BTLA has been linked to T cell dysfunction during cancer, and dual blockade of BTLA and PD1 improves antitumor immunity. |
The human BTLA gene encodes a 289-amino acid type I glycosylated transmembrane protein. BTLA is composed of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM) as well as a growth factor receptor-bound protein-2 (Grb-2) recognition motif in its cytoplasmic domain.
BTLA is expressed in most lymphocytes (such as B cells, T cells, and Tregs). It is expressed at different levels in some cells, for example, highly expressed in the B-lymphocytes, splenic macrophages, and bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. The expression in CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells is much lower. Additionally, BTLA can also be expressed in NK cells, NKT cells, and myeloid cells.
BTLA plays an essential role in inducing and maintaining T-cell immune tolerance by inhibiting TCR signaling-mediated T-cell proliferation, activation, and cytokine production. Moreover, HVEM-BTLA signaling could maintain the stability of the internal environment for DCs. And for the BCR signaling pathway, BTLA partially but not completely inhibits B cell function. Thus, the BTLA is being considered as a new target to develop immune checkpoint blockade for cancer therapy.
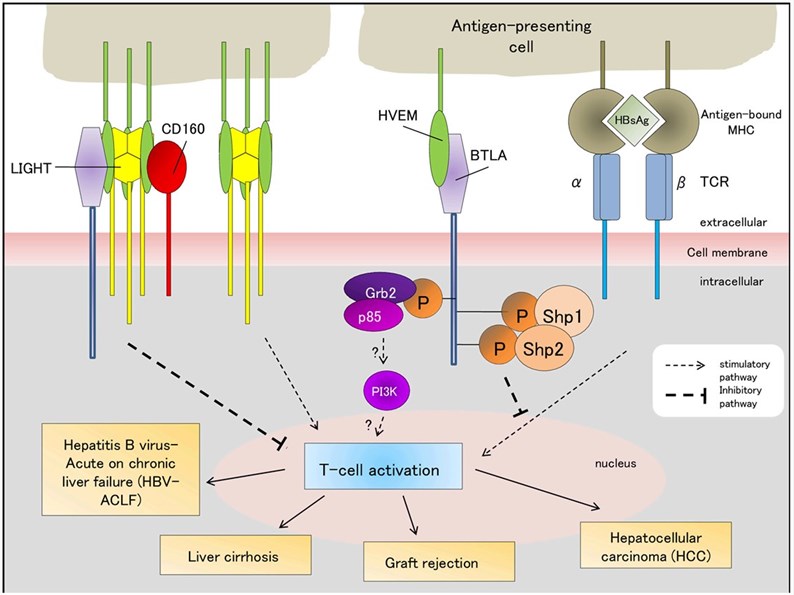 Fig.1. BTLA-associated signaling pathways.1,2
Fig.1. BTLA-associated signaling pathways.1,2
Since the discovery of BTLA, multiple studies have revealed that the immune checkpoint molecule BTLA plays an essential immunomodulatory role in many diseases, including but not limited to autoimmune disease, cancer, transplantation, infection, and other conditions. The therapeutic strategies that target the BTLA using specific antagonist antihuman antibodies have been published in numerous patents. Simultaneously, targeted anticancer drugs for BTLA-associated signaling pathways are emerging and currently in some preclinical and clinical trials. It is predicted that targeting BTLA will lead to a new revolution in unraveling the immune mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of many diseases.
By partnering with Creative Biolabs, you gain scientific support that increases your research potential to be successful. A series of custom services for immune checkpoint BTLA is available at Creative Biolabs, including but not limited to:
If you want to learn more detailed information, please feel free to contact us.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.