Butyrophilin-like 2 (BTNL2), a protein belonging to the butyrophilin-like (BTNL) protein family, provides the inhibitory signal to T cells and is involved in multiple inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. As is typical of the butyrophilins, no protein-ligand has been identified, although a BTNL2-Fc fusion protein is shown to bind to activated lymphocytes. Manipulation of the molecular interaction of BTNL2 with its putative receptor could provide strategies to restore immune homeostasis in these diseases.
Table.1 Immune checkpoint BTNL2.
| Immune Checkpoint | Alternate name | Expression | Ligand | Function |
| BTNL2 | BTL-II/BTN7 | BTNL2 expression is found in lymphoid organs and nonlymphoid organs, most abundantly in the intestine. | Unknown | Inhibit T-cell proliferation |
The extracellular region of BTNL2 comprises multiple immunoglobulin variable (IgV) and immunoglobulin constant (IgC) domains, followed by a single-pass transmembrane region and a short cytoplasmic region. Unlike most other butyrophilin and butyrophilin-like members, BTNL2 does not contain the cytoplasmic signaling domain. The N-terminal ectodomain of BTNL2 can inhibit T cell function and exhibit distinctive structural features.
BTNL2 is expressed on the surface of B cells, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells upon activation. It recognized a putative receptor whose expression on B and T cells is significantly enhanced after activation. BTNL2 expression is found in lymphoid organs and nonlymphoid organs, most abundantly in the intestine. Abundant expression of BTNL2 mRNA in the intestine may suggest the important function of BTNL2 in regulating mucosal immunity or tolerance.
BTNL2, which is the first member of the butyrophilin family regulating T cell activation, binds to a putative receptor on activated T cells and functions to inhibit the proliferation of T cells. BTNL2 acts as a T cell inhibitory molecule that can induce FoxP3+ Treg differentiation, effectively suppressing effector T cells during inflammation. Such action by BTNL2 has the potential to be manipulated to either induce immune suppression during unwanted autoreactive responses or to trigger more robust immune responses in the tumor microenvironment.
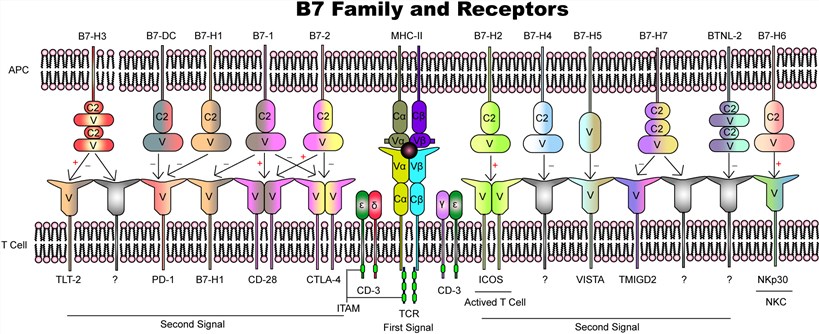 Fig.1. B7 family members and their receptors.1,2
Fig.1. B7 family members and their receptors.1,2
BTNL2 is a potential therapeutic target for restoring immune tolerance under inflammatory conditions and manipulation of BTNL2-mediated immune response for the development of novel therapeutics. In addition, recombinant BTNL2-Ig is now regarded as a potential treatment for patients with graft-versus-host disease. Much more work needs to be performed by using specific Abs to BTNL2 and by gene-targeting animals to illustrate the in vivo possible function of BTNL2 in immune tolerance.
Creative Biolabs is a well-recognized expert who supports a broad range of drug development projects for immune checkpoints. Currently, a series of custom services for immune checkpoint BTNL2 is available at Creative Biolabs, including but not limited to:
Please do not hesitate to contact us for more detailed information.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.