Emerging as a cancer therapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) require constant patient monitoring to address adverse reactions, including immune-related events and unconventional responses. Biomarkers, which indicate structural or functional changes in various biological systems, organs, tissues, and cells, offer a means to predict and tailor treatments for such reactions. These anti-tumor immunotherapy biomarkers can originate from tumors (e.g., negative regulatory molecules and genome sequence alterations) or the immune system (e.g., peripheral blood cell counts, cytokines, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and gut microbiota). The development of biomarkers plays a crucial role in assessing treatment efficacy, predicting adverse reactions, and forecasting disease progression, while also considering the impact of organ toxicity and systemic events on ICI therapy.
As multiplex immunohistochemical technology, high-throughput sequencing, and microarray technology have evolved and continually improved, an array of biomarker strategies has surfaced, transitioning from the discovery of singular markers to the advancement of multifaceted synergistic predictive markers. The evolution of predictive biomarkers has played a pivotal role in unveiling the therapeutic intricacies of ICIs and elucidating the interplay between tumor and host immunity.
In conclusion, Creative Biolabs paid attention to customization of anti-tumor immunotherapy, enabled efficacy monitoring and disease progression assessment, steered the design of preclinical trials, and fostered a deeper comprehension of drug resistance mechanisms and tumor prognostication for our customers.
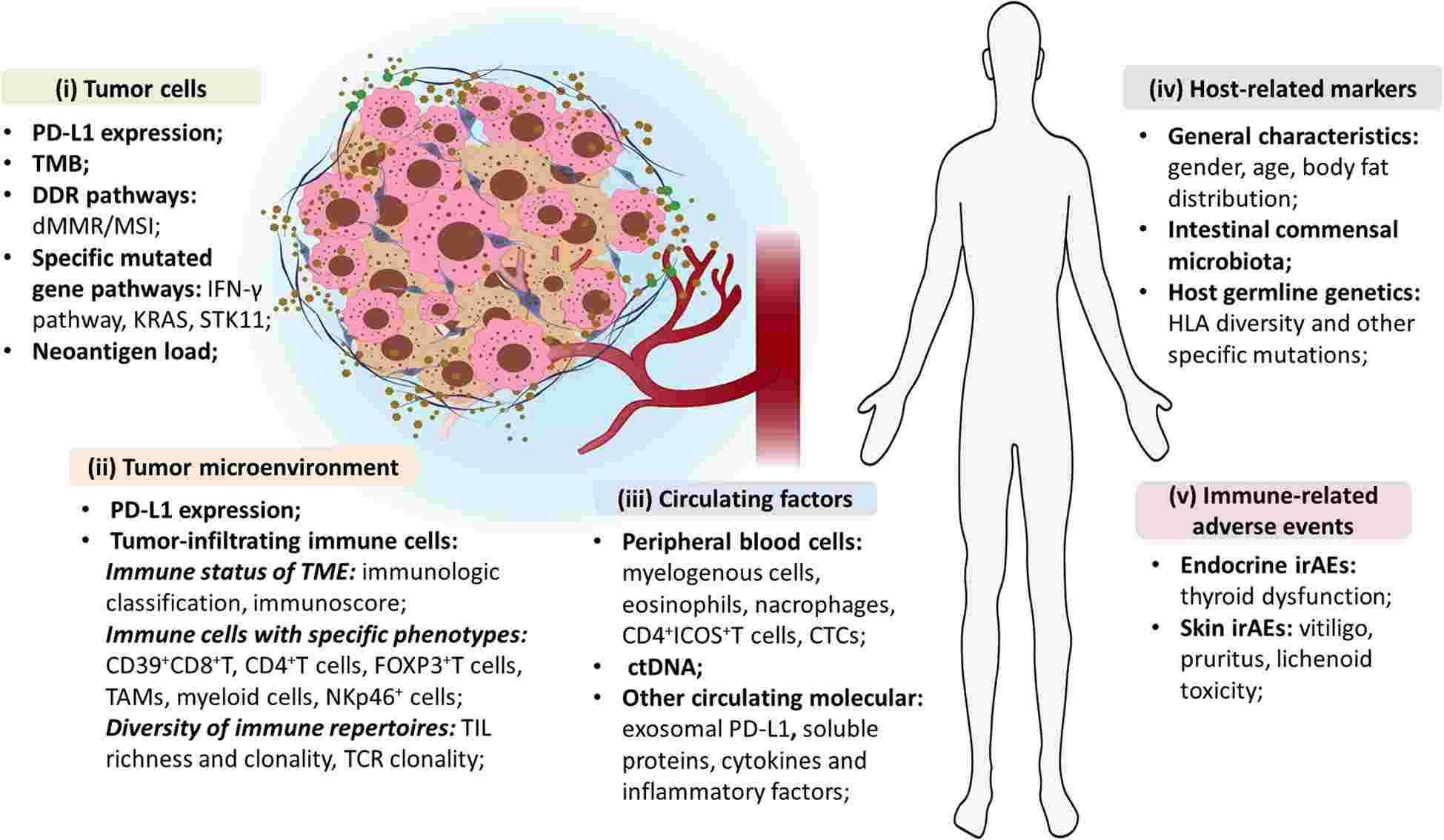
|
Fig.1. Comprehensive insights into predictive biomarkers of efficacy for ICIs.1,3 |
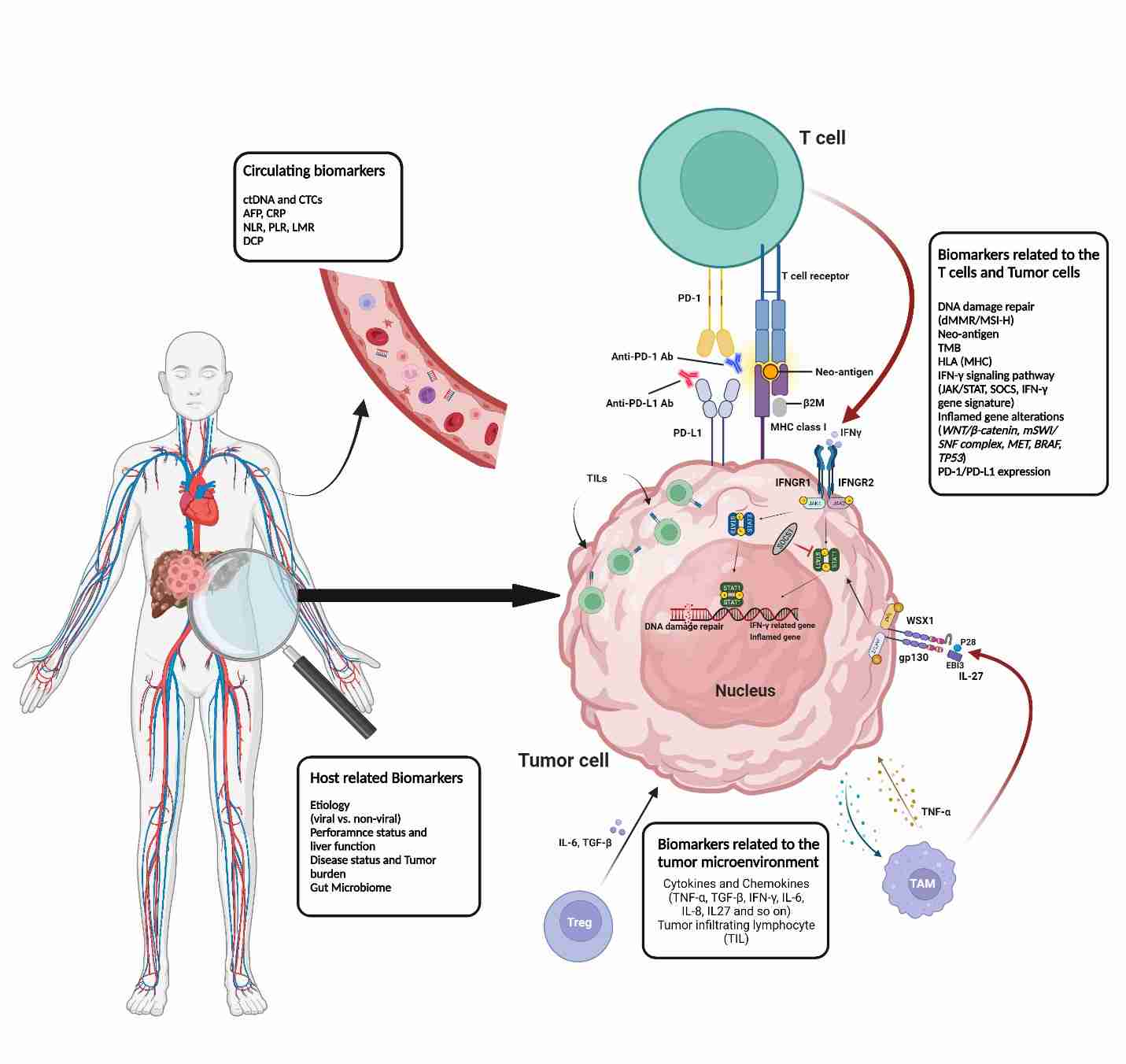
|
Fig.2. Illustrative diagram depicting predictive biomarkers in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).2,3 |
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of customized services related to immune checkpoints, including but not limited to: Custom Immune Checkpoint Protein Development, Antibody Development for Immune Checkpoints, Immune Checkpoint Targeted Peptide Development, Immune Checkpoint Targeted Small Molecule Drug Development, Biomarker Development for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI), etc. For a comprehensive overview, please do not hesitate to contact us.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.