Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy has the capacity to induce long-lasting clinical responses through the reactivation of a fatigued immune response. Nevertheless, the efficacy of single ICB therapy is constrained by the absence of a tumor-responsive immune infiltrate. Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy offers an effective solution to this limitation by furnishing the essential tumor-targeting immune infiltrate and a precision-oriented antitumor immune response. Augmentation of CAR-T cell therapy's effectiveness can be achieved by the incorporation of ICB agents, which can counteract the immune-inhibitory milieu that hampers the optimal efficacy of CAR-T cells.
CAR-T cell therapy has exhibited efficacy across a spectrum of malignancies, harnessing the immune system's prowess for cancer cell recognition and eradication. Nevertheless, when employed as standalone treatments, their therapeutic impact is less pronounced. Growing substantiation indicates that tumors can elude immune scrutiny by provoking inhibitory immune checkpoint receptors on T cells, encompassing CTLA-4 and PD-1. Such provocation gives rise to an immunosuppressive microenvironment that curtails the effectiveness of CAR-T cell therapy. Hence, the utilization of antibodies to obstruct these inhibitory immune checkpoints emerges as a promising strategy for augmenting the favorable outcomes of CAR-T treatment in solid tumors.
The exploration of combinatory therapeutic approaches involving CAR‑T cell interventions and ICB has been extensively investigated in preclinical investigations, demonstrating promising outcomes. The synergy between CAR-T cell therapy and ICB has exhibited remarkable potential, culminating in sustained survival without manifesting any discernible pathological manifestations in vivo.
|
|
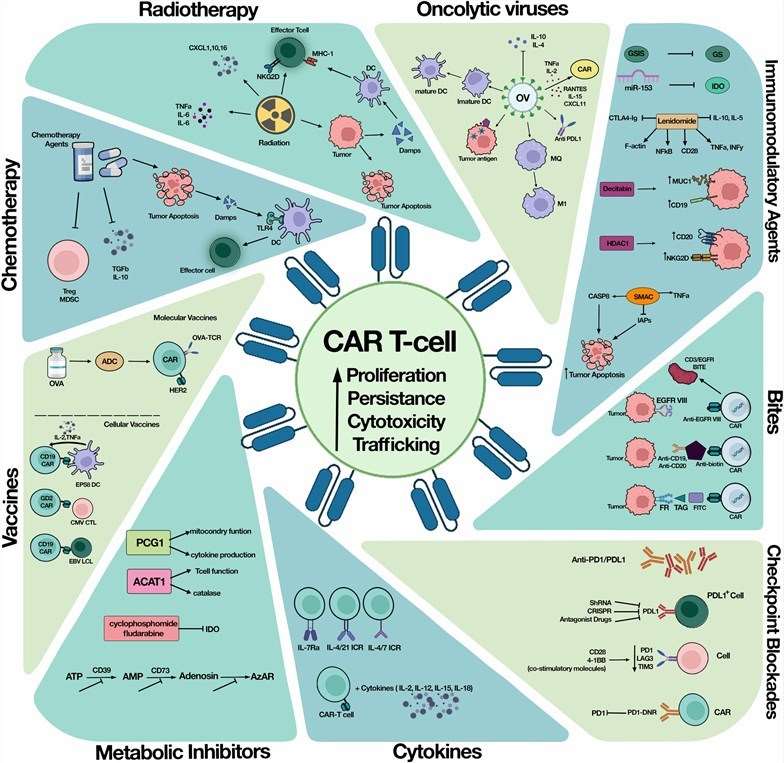
| Fig.1. Immune checkpoint inhibition with CAR-T cell combination therapy.1,3 | |
|
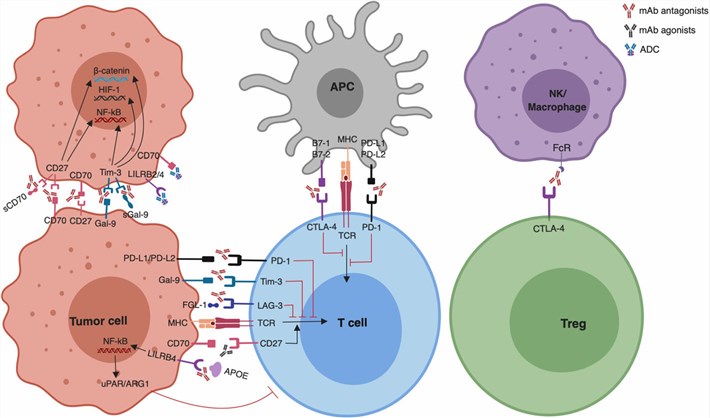
Fig.2. The application of ICB and other therapies in hematologic malignancies.2,3 |
Immune checkpoint molecules have been regarded as new targets for combating cancer, sparking significant enthusiasm in the realms of biological and preclinical investigations when integrated with CAR-T cell therapy.
Creative Biolabs extends an exhaustive suite of tailored, top-tier offerings encompassing immune checkpoint antibodies, proteins, peptides, assays, and small molecule drug development, with the aim of bolstering the pharmaceutical sector and the interconnected research communities in biomedical sciences worldwide. Our seasoned team with boasting years of expertise, stands ready to collaborate with you to ensure the products developed align precisely with your requisites:
Contact us for details.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.