An interesting new member of the immune checkpoint family is the macrophage immune checkpoint SLAMF3/4. As a leading expert in the field of immune checkpoints, Creative Biolabs provides resources on SLAMF3/4, sharing its importance, molecular mechanism, and potential impact on therapeutic development.
SLAMF consists of nine cell surface receptors involved in the regulation of immune cell activation. These molecules are expressed to varying degrees on a wide range of immune cell types.
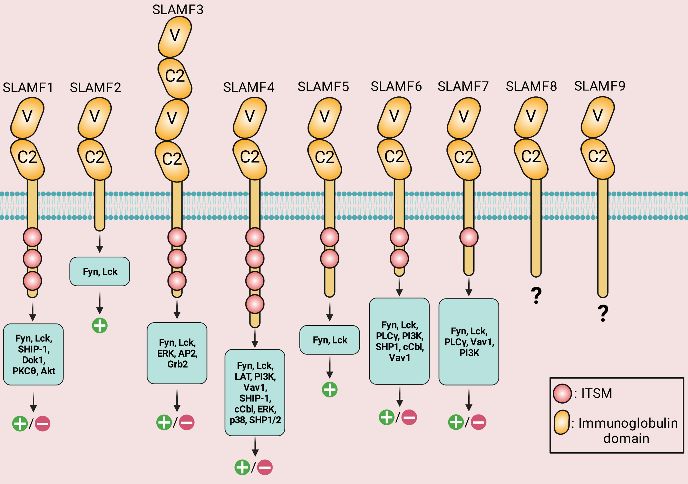 Fig.1. Structure of SLAMF receptors.1,2
Fig.1. Structure of SLAMF receptors.1,2
SLAMF3 and SLAMF4, also known as CD229 and CD244, respectively, belong to the SLAM family. Originally identified as T cell and NK cell markers, these receptors were later found to be expressed on macrophages, revealing their role in regulating macrophage function.
The SLAMF3/4 immune checkpoint orchestrates the macrophage response through complex molecular interactions. These interactions trigger downstream signaling pathways that can either enhance or inhibit macrophage activation, depending on the context.
The dual role of SLAMF3/4 in enhancing and inhibiting macrophage function suggests a dynamic regulatory mechanism adapted to different immune challenges.
The discovery of SLAMF3/4 as a macrophage immune checkpoint opens up exciting avenues for therapeutic intervention. Harnessing the potential of immune checkpoints may yield new strategies for treating a range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory diseases.
The CD47/SIRPα signaling pathway is a classical pathway regulating phagocytosis in macrophages. In contrast, the SLAM family of receptors may represent a specific receptor and is expected to provide new targets for tumor immunotherapy.
Creative Biolabs recognizes the importance of this emerging immune checkpoint and its potential for therapeutic applications. As our research progresses, we will explore and capitalize on these cutting-edge discoveries. If you have a research need, please contact us.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.