Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are cells isolated from primary tumors and circulating in the bloodstream. As a potentially rich source of information, they can provide insight into tumor biology and progression. Unraveling the immune checkpoints in CTCs provides a deeper and more nuanced understanding.
Creative Biolabs explores immune checkpoints on CTCs, which can provide valuable information about the interactions between cancer cells and the immune system, potentially guiding personalized therapeutic strategies.
CTCs can play an important role in the metastatic spread of cancer by reaching distant sites through the bloodstream and triggering the formation of secondary tumors. Immune cells can recognize and target a small fraction of CTCs for destruction. However, some CTCs may express immune checkpoint ligands that bind to immune checkpoint receptors on immune cells, leading to immunosuppression and reduced tumor cell killing.
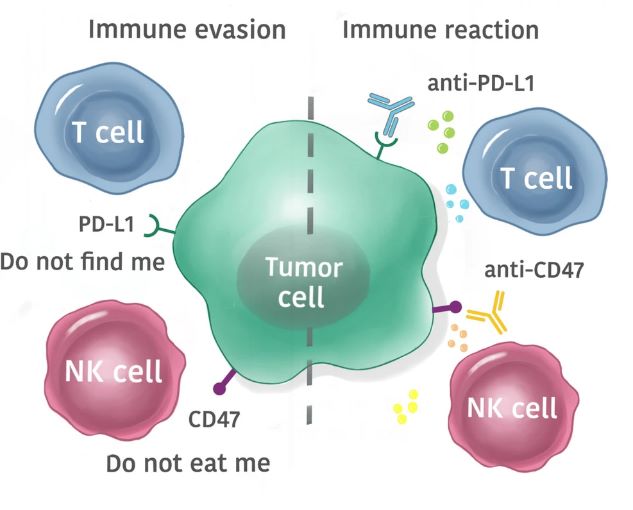 Fig.1. Immune checkpoint therapy targeting circulating tumor cells. 1,2
Fig.1. Immune checkpoint therapy targeting circulating tumor cells. 1,2
Researchers are exploring the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors to target CTCs and prevent them from escaping immune surveillance. By blocking the interaction between immune checkpoints on CTCs and immune cells, the immune response against these circulating cancer cells could be enhanced and the risk of metastasis reduced.
Identifying immune checkpoints in CTCs is a multifaceted and complex affair. First, multiple biomarkers are often employed to distinguish CTCs from normal cells that share their environment. Flow cytometry, digital pathology, and immunocytochemistry are standard techniques in CTC identification. Increasingly, finer techniques are being fully utilized.
Although the identification of immune checkpoints in CTCs is an emerging field with great potential, several challenges remain.
By elucidating the complex interplay between immune checkpoints and CTCs, researchers are paving the way for personalized therapeutic strategies that exploit these checkpoints to overcome immune evasion. Creative Biolabs is also continuously advancing the immune checkpoint research of CTC.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.