In the intricate field of immune regulation, LAG-3 is a key immune checkpoint receptor that influences the balance of T-cell activity. LAG-3 inhibitors have emerged as a compelling avenue for immunotherapy. Creative Biolabs delves into the fascinating world of LAG-3 inhibitors and their potential for revolutionizing cancer treatment.
LAG-3 functions as a crucial brake on the immune system, preventing excessive activation and ensuring immune homeostasis. However, cancer cells have devised sophisticated strategies to exploit this mechanism, effectively evading immune surveillance and perpetuating their growth. By engaging with its ligand, LAG-3 acts as a gatekeeper, impairing T cell responses and dampening the immune system's ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells.
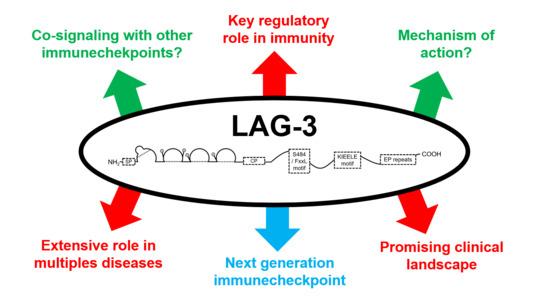 Fig.1. Understanding LAG-3 signaling.1,2
Fig.1. Understanding LAG-3 signaling.1,2
LAG-3 inhibitors, specifically designed molecules that target and block the LAG-3 receptor, offer a means to release the brakes on the immune system and unleash its full anti-tumor potential. The potential of LAG-3 inhibitors extends beyond their direct effects on T cell activity. They can reshape the tumor microenvironment by disrupting the immunosuppressive network orchestrated by cancer cells.
LAG-3 inhibitors have been explored across diverse malignancies, offering hope for targeted therapeutic interventions.
LAG-3 inhibitors have promise across multiple cancer types. The intricate interplay between LAG-3 and the tumor microenvironment holds the key to unraveling their efficacy in each specific context.
In the quest to harness the full potential of LAG-3 inhibitors, researchers have explored various strategies and developed innovative therapeutic molecules.
LAG-3 inhibitor research is a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape, with numerous inhibitors currently under development.
The landscape of LAG-3 inhibitor development is teeming with excitement and potential. At Creative Biolabs, our experienced service team provides a full range of research services for the development of LAG-3 inhibitors for our clients worldwide. Please don't hesitate to contact us.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.