B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) was initially identified as a critical regulator of apoptosis, the programmed cell death that maintains tissue homeostasis. Its primary role was considered anti-apoptotic, as it prevents cells from undergoing apoptosis, a process that is often exploited by cancer cells to survive and proliferate unchecked.
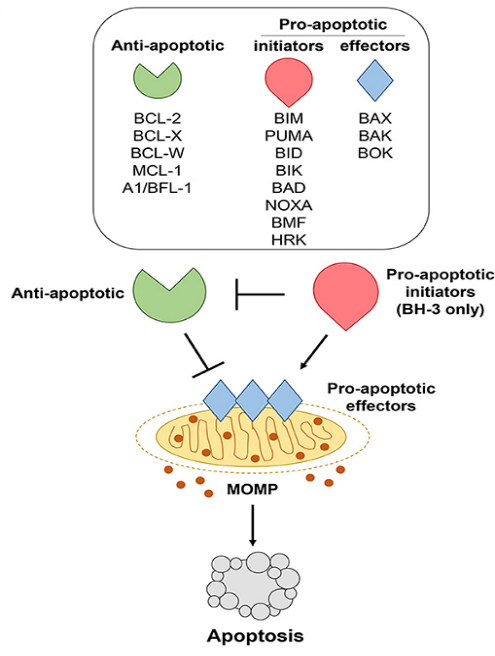 Fig.1. Bcl-2 family members regulate apoptosis.1,2
Fig.1. Bcl-2 family members regulate apoptosis.1,2
However, recent research has unveiled a surprising twist in BCL-2's narrative—it also appears to have an immunosuppressive role, thereby emerging as a potential immune checkpoint.
Cancer cells constantly devise new strategies to evade the immune system's surveillance. One such strategy involves hijacking the BCL-2 pathway. BCL-2 overexpression in cancer cells not only promotes their survival by resisting apoptosis but also exerts a suppressive effect on immune cells.
Traditionally, BCL-2 has been recognized for its role in preventing apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in normal cells. However, recent studies have illuminated the discovery of BCL-2's involvement in immune regulation, which has opened up new avenues for research and therapeutic development.
BCL-2 hampers the immune response through various mechanisms, making it a formidable immune checkpoint.
Researchers are now exploring strategies to harness the potential of BCL-2 inhibition in the fight against cancer.
In conclusion, the emergence of BCL-2 as a novel immune checkpoint represents a paradigm shift in cancer immunotherapy. Unlocking the potential of BCL-2 inhibition offers new hope in the battle against cancer.
At Creative Biolabs, we remain committed to exploring innovative strategies to target BCL-2 and elevate the prospects of successful cancer immunotherapy.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.