Immune checkpoint therapies are challenged by low response rates, innate or acquired resistance, and immunotherapy-related adverse events that challenge the utility of clinical application. Therefore, the discovery of novel strategies that can be combined with ICI is crucial.
The functions of m6A modifications and immune checkpoints have been extensively studied in recent decades. A range of immune checkpoints have been reported to be supervised in an m6A-dependent manner. Creative Biolabs describes recent advances in understanding the molecular mechanisms behind m6A-modified immune checkpoints.
The m6A modification is a dynamic RNA epigenetic mark located in complex molecular biological structures. This chemical modification involves adenosine methylation at the N6 position within the RNA molecule. It plays a key role in the regulation of gene expression, RNA processing, and ultimately protein translation.
The m6A modification acts as a finely regulated molecular switch that determines when and how genes are expressed. Recent studies have revealed its involvement in a wide range of biological processes, including cell differentiation, stress response and immunity.
One of the remarkable features of m6A modification is its role in shaping the immune response. It significantly affects the expression of immune checkpoint molecules and influences the outcome of immune checkpoint therapy. By modifying the RNA transcripts of checkpoint genes, m6A can either enhance or block their translation. m6A modifications play a dual role in cancer.
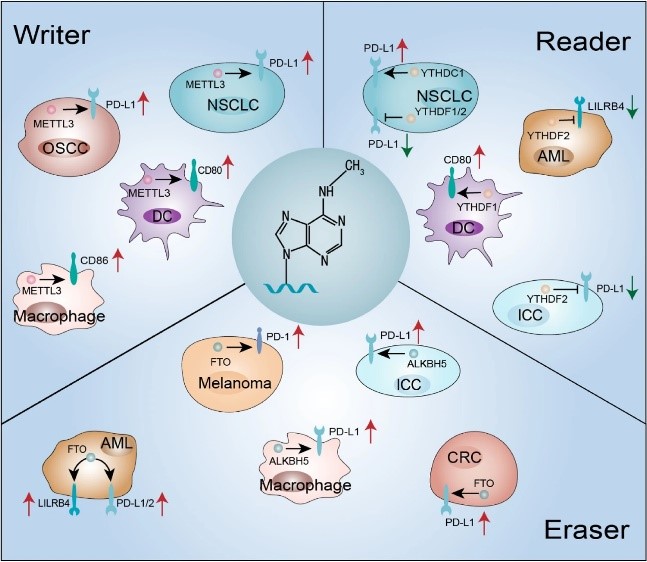 Fig.1. m6A regulatory factors alter immune checkpoint expression in tumors.1,2
Fig.1. m6A regulatory factors alter immune checkpoint expression in tumors.1,2
Scientists are exploring various strategies to capitalize on the potential of m6A modifications to enhance the effectiveness of immune checkpoint therapy.
As researchers continue to unravel the complexity of how m6A modifications affect the immune checkpoint pathway, the potential for innovative and more effective cancer therapies becomes increasingly apparent.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.