Tumor-associated macrophages are an important part of the tumor microenvironment, and targeting their immune checkpoints has excellent anti-tumor potential, and they have emerged as potential targets in cancer therapy. Here, Creative Biolabs highlights some macrophage-associated immune checkpoint proteins, and related development services can be customized by contacting us.
Macrophage function is tightly controlled by many negative regulators that directly inhibit or divert their effector functions. Some of these molecules, such as SIRPα, Siglec and members of the LILRB family are known as myeloid immune checkpoints. These pathways are physiologically used to protect host tissues from unwanted attacks, leading to a state of immunosuppression and activation of the trophic function of TAM tissues, which may ultimately be hijacked by tumor cells to evade recognition by the immune system and proliferation.
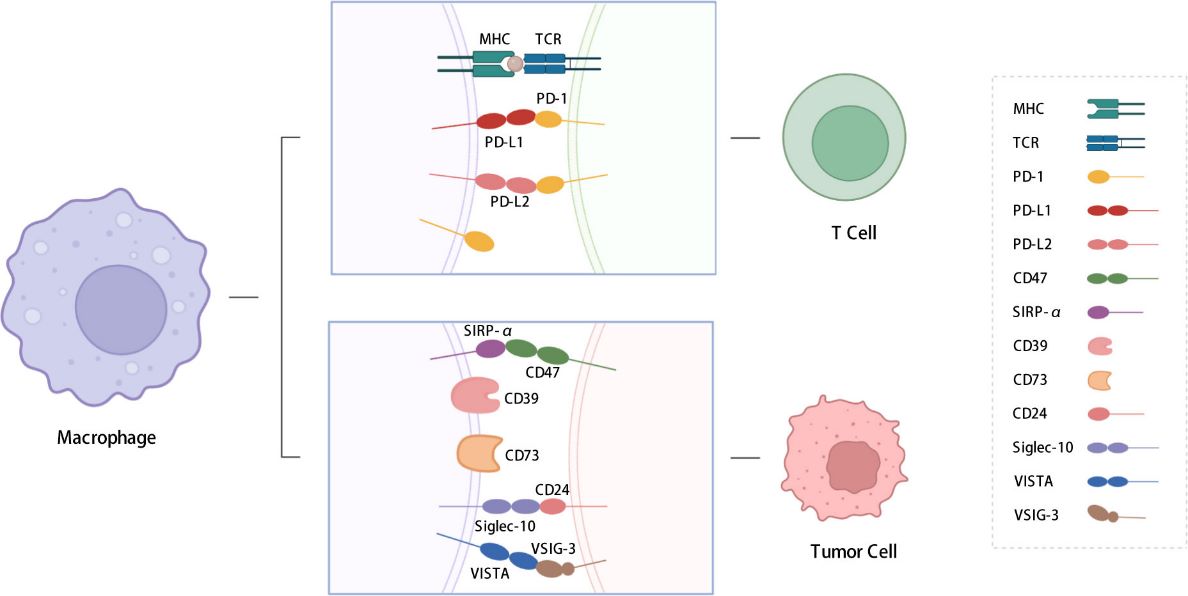 Fig.1. Immune checkpoints expressed on macrophages.1,2
Fig.1. Immune checkpoints expressed on macrophages.1,2
Several potential therapeutic agents have been developed to target CD47, including antibodies, small molecules, siRNAs and peptides.
Siglecs are a family of receptors that bind to salivary acid-containing glycans, and 15 human and 9 murine Siglec molecules have been identified. Macrophages highly express several different Siglec receptors, including Siglec-3, Siglec-5, Siglec-7, Siglec9, Siglec-10, Siglec14, and Siglec-15.
Siglec molecules intracellularly contain immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motifs (ITIM), which are usually components of those immunoreceptors that inhibit and suppress activating signals, thereby regulating the function of a wide range of immune cells.
LILRB is a class of primary transmembrane glycoproteins that have immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) structural domains in the extracellular region and ITIM motifs in the intracellular region.
To aid in the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors, Creative Biolabs offers customized services to develop a range of high-quality macrophage immune checkpoint proteins, including CD47, SIRPα, CD24, Siglec-10, LILRBs, and others. Do not hesitate to contact us.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.