Non-specific immune overactivation may lead to severe RA. Creative Biolabs aims to expand your understanding of RA through our theoretical support and successfully manage its toxicity and clinical manifestations by utilizing knowledge related to immune checkpoint modulation.
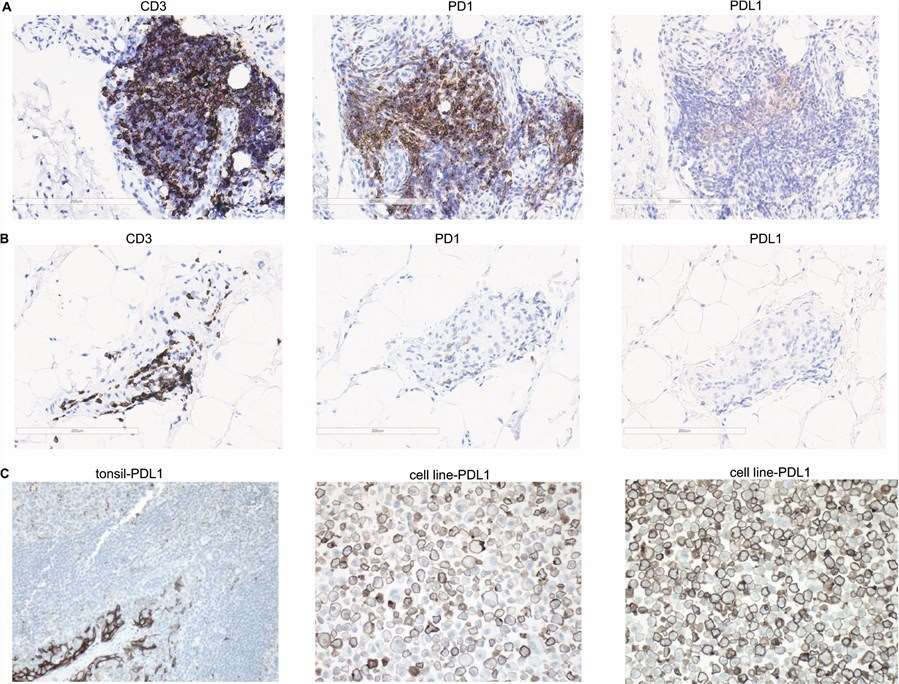 Fig.1. RA and immune checkpoint molecules.1,3
Fig.1. RA and immune checkpoint molecules.1,3
RA is an autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized by joint dysfunction and disability. During the pathogenesis of RA, immune checkpoint molecules interact with key cytokines such as TNF-α/IL-6, thereby regulating the immune mechanisms of RA and influencing its clinical disease activity and joint damage.
Currently, immune checkpoint therapy is considered a double-edged sword - it activates immune cells to attack cancer cells but also unleashes the potential of autoreactive T cells. In fact, RA has become one of the more common and well-documented immune-related adverse events in patients receiving anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 treatments.
In fact, several key immune checkpoint molecules have been confirmed to be directly associated with RA, and deepening the understanding of these checkpoints would be beneficial for preventing or intervening in the pathological processes of RA.
| Association of Immune Checkpoint Pathways with RA | |
| Co-Stimulatory | CD28-CD80/86, CD27-CD70, CD40-CD40L,4-1BB-4-1BBL… |
| Co-Inhibitory | TIGIT-CD115/112/226, PD1-PDL1/2, CD200-CD200R… |
| Others | CD38, IDO… |
Targeted therapies occupy a higher position in the pyramid of RA interventions. Currently, there are very few immune checkpoint-based approaches directly targeting the pathology of RA, and the majority of preclinical achievements have been tested in the mouse collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model:
Title: Association between inflammatory cytokines and immune-checkpoint molecule in rheumatoid arthritis.
Research Objective:
To investigate the impact of combined biomarkers such as autoantibodies, cytokines, and immune checkpoint molecules on the progression of RA.
Methodology:
Serum cytokines and immune checkpoint molecules were evaluated in RA patients with different disease progression and severity. Serum IL-6, TNF-α, Gal-9, and TIM-3 levels were measured using a sandwich ELISA method.
Research Findings:
It was observed that IL-6 was positively correlated with Gal-9 in RA patients without severe symptoms, while the correlation between TNF-α and Gal-9 was confirmed in patients with severe joint damage. This demonstrates that immune checkpoint molecules may regulate the immune pathology of RA through interaction with cytokines and could be potential effective targets for intervention in RA.
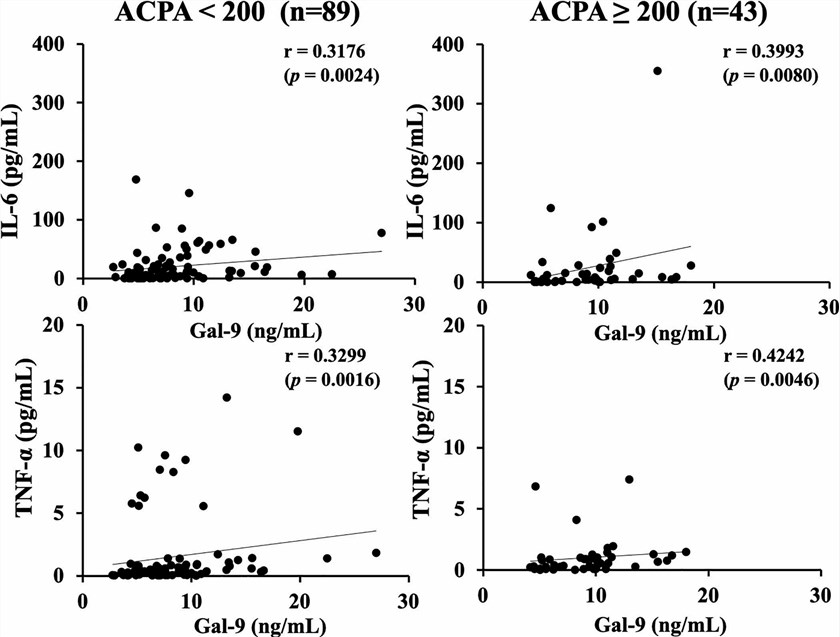 Fig.2. Significant correlation between serum cytokines and GAL-9 levels.2,3
Fig.2. Significant correlation between serum cytokines and GAL-9 levels.2,3
At Creative Biolabs, we offer comprehensive services beyond theoretical support. With our unwavering commitment to excellence, we strive to provide unmatched support and expertise to help you effectively uncover the puzzle of immune checkpoints. Our team of experts is dedicated to delivering exceptional services tailored to your requirements.
We invite you to contact us today to collaborate with our team of experts and transform your research goals into reality.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.