The growing interest in checkpoint inhibitors from the pharmaceutical industry requires a suitable model for target discovery and preclinical evaluation. Although the human tumor transplantation models relying on immunodeficient mice have been widely used in the development of new therapies targeting cancers. There are significant differences existing between the human and mouse immune systems, and the lack of the human immune system and tumor immune microenvironment largely limits the translational research of immune mechanisms and immunotherapy.
The human immune system mouse model is a kind of mouse model that translates human immune cells or tissues (such as lymphocytes, hematopoietic cells, or thymic tissue) into severely immunodeficient mice to reconstruct the human immune system in mice. In this mouse, human protein structure and function may share sufficient homology with their mouse equivalents, thus making the preclinical evaluation of antibodies targeting human checkpoint molecules practically realizable.
According to the establishment method, mouse models of the human immune system can be divided into three types:
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) are a kind of mixed cell population in peripheral blood. These cells have only one nucleus and are mainly composed of monocytes, phagocytes, dendritic cells, T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and NK cells. It is a crucial cell component of the immune response. Mature lymphocytes derived from PBMC were injected intravenously or intraperitoneally into severe immunodeficient host mice to establish Hu-PBMC mouse models. Hu-PBMC mouse model is a comparatively simple and economical humanized mouse model and is usually used to study the activation of human effector T cells and to evaluate the function of some immunosuppressive drugs. Furthermore, transplantation of human PBMCs or enriched immune subsets, such as T cells, into CDX/PDX models could provide targets for checkpoint inhibitors.
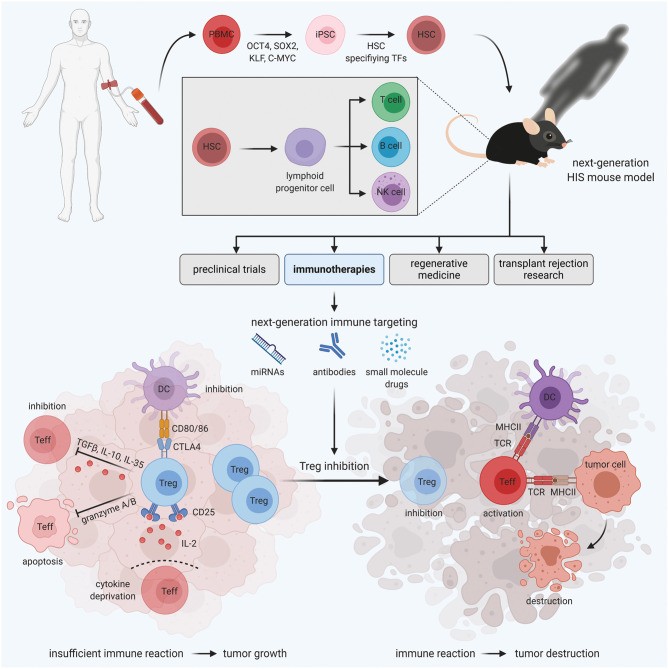 Fig.1. The function and establishment method of the human immune system mouse model.1,2
Fig.1. The function and establishment method of the human immune system mouse model.1,2
Hu-HSC mice are referred to as severely immunodeficient mice carrying human immune cell lineages derived from transplanted hematopoietic stem cells. In comparison to PBMC mice, human T cells developed in human immune system mice are negatively selected on mouse thymus and therefore tolerant to mouse peripheral tissues. Nevertheless, human T cells selected in mouse thymus do not efficiently initiate antigen-specific responses.
In the Hu-BLT mouse model, immunodeficient mice are treated with sublethal doses of irradiation, and then human fetal liver and thymus tissue are transplanted under the renal capsule of adult immunodeficient recipient mice. At the same time, bone marrow-derived CD34+ or fetal liver from the same individual HSCs are injected intravenously into the recipient mouse. The transplantation of the human fetal liver and thymus creates a human thymic microenvironment that facilitates the growth and differentiation of human T cells. These T cells encompass a wide range of HLA-restricted varieties, enabling them to initiate an effective adaptive immune response. Consequently, the BLT model serves as a valuable tool for studying adaptive immune responses, including those connected to HIV infection. Nevertheless, there are challenges in matching the tumor cells and immune system from the same donor, and the establishment of the Hu-BLT model necessitates intricate and intricate surgical procedures. As a result, the application of the Hu-BLT model in the development of tumor immunotherapy drugs is constrained.
Creative Biolabs is a well-known biotechnology company that has been at the forefront of research in life sciences. Our expert team has been engaged in tumor immune checkpoint and drug development for many years, with sufficient professional knowledge and experience, and we can provide high-quality related products. If you are seeking a specialized and responsible partner, we will be your best choice. We offer the following integrated oncology immune checkpoint services:
You can click on our Services Overview for more information, and contact us whenever you need, we are honored to serve you.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.