Immune checkpoints are crucial molecules for fine-tuning immune responses and play a significant role in cancer immunotherapy. As a leader in immunotherapy development, Creative Biolabs is uniquely positioned to address the demands of immune checkpoint protein development with our unparalleled, multiplexed protein expression platform. Our comprehensive services include immune checkpoint stable cell line development and immune checkpoint protein labeling.
Immune checkpoint is a kind of regulatory molecule in the immune system that is crucial for self-tolerance, which prevents the immune system from attacking cells indiscriminately. Immune checkpoint proteins play an important role in cancer immunotherapy research, and they function as co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory signals to enhance or inhibit immune responses. Targeting immune checkpoints by strengthening the immune response by agonists of co-stimulatory signals or antagonists of co-suppression signals is a novel strategy to attack tumor cells and treat cancers. Immune checkpoints can be divided into two kinds of signals: 1) Co-stimulatory immune checkpoints, stimulating immune responses, such as CD27, CD40, OX40, GITR, 4-1BB, CD28, ICOS, etc.; 2) Co-inhibitory immune checkpoints, inhibiting immune responses, such as PD1, PD-L1, CTLA-4, VISTA, CD155/TIGIT, TIM-3, etc.
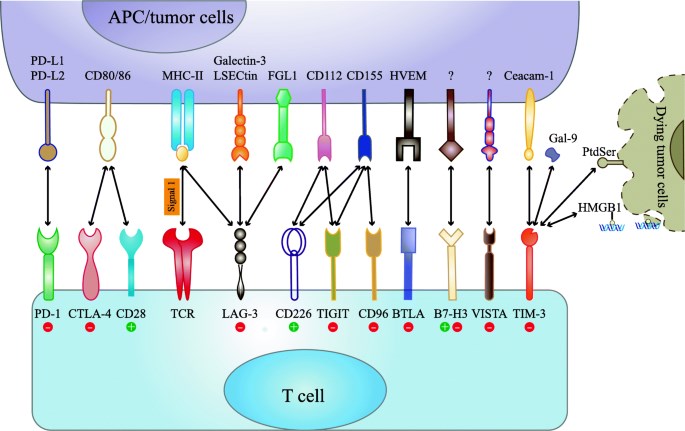 Fig.1. Immune checkpoint receptors and their respective ligands.1,2
Fig.1. Immune checkpoint receptors and their respective ligands.1,2
With an improved understanding of immune checkpoint pathways, Creative Biolabs has tremendous efforts to discover numerous immune checkpoint proteins as potential anti-cancer therapy targets. We discover and express many checkpoint proteins that are often engaged by cancer cells to alter activation pathways and ultimately attenuate the immune response, which are promising druggable protein targets in cancer treatment. Besides the identification, discovery, and characterization of checkpoint proteins, we also developed stable cell line development and immune checkpoint protein labeling services to meet downstream demands.
 Stable cell lines have a variety of applications, such as gene functional studies and binding/blocking screening. Based on the common checkpoint proteins (such as PD1, PD-L1, CTLA-4, VISTA, Tim3, and Lag3), we have developed high-quality stable cell lines expressing immune checkpoints to accelerate your immunotherapy discovery. Our stable cell lines allow for high-throughput assays, the overexpression of the respective marker checkpoint protein, and screening of high-affinity antibodies against immune checkpoint proteins. Stable cell lines have a variety of applications, such as gene functional studies and binding/blocking screening. Based on the common checkpoint proteins (such as PD1, PD-L1, CTLA-4, VISTA, Tim3, and Lag3), we have developed high-quality stable cell lines expressing immune checkpoints to accelerate your immunotherapy discovery. Our stable cell lines allow for high-throughput assays, the overexpression of the respective marker checkpoint protein, and screening of high-affinity antibodies against immune checkpoint proteins.
|
| Protein labeling technology offers an alternative to fluorescent proteins for studying the function of proteins in living and fixed cells. With abundant expertise in protein engineering, we provide the optimal solution and specialized service to successfully meet your immune checkpoint protein labeling requirements. For example, our biotin-labeled checkpoint proteins can be used for ELISA, SPR, and FACS experiments with low background, highly specific, high bioactivity, and minimal batch-to-batch variation. |

|
The immune checkpoint protein development can largely facilitate the research of antitumor immunity. We have expressed active immune checkpoint proteins and related stable cell lines confirmed by our strict quality control. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2025 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.