The immune inhibitory checkpoints play essential roles in mediating immune tolerance and protecting tissues from collateral damage. Two important immune checkpoint receptors, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death protein 1 and its ligand (PD-1 / PD-L1), have been widely studied in clinical cancer immunotherapy. In addition to checkpoints that suppress T-cell responses, the antiphagocytic signal CD47 has emerged as a key stimulatory checkpoint of innate immunity in clinics. Creative Biolabs combines the most extended range of services and the best experts for immune checkpoint antibody development and will put the necessary resources and solutions to deliver the perfect immune checkpoint antibody humanization services.
Methods of antibody humanization are designed to produce a molecule with minimal immunogenicity when applied to humans while retaining the specificity and affinity of the parental non-human antibody. The leading technologies of antibody humanization include: 1) in vitro complementarity-determining region (CDR) grafting of murine antibodies onto human frameworks; 2) in vitro systems such as phage display libraries; 3) in vivo immune systems of "humanized" host genetically engineered to express a human immunoglobulin repertoire.
Creative Biolabs provides antibody humanization services for mouse, rat, rabbit, chicken, and camelid antibodies. Our proprietary technologies can incorporate the sequences of the antibody variable domains into human donor sequences and rapidly produce cell lines for expressing humanized antibodies.
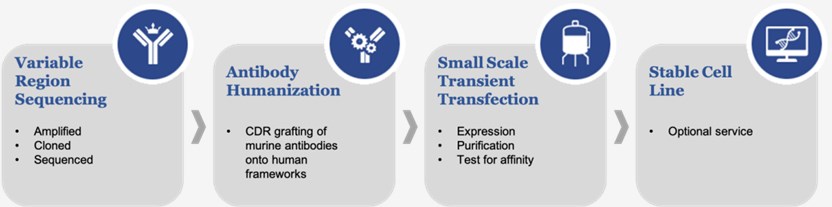
A common method for the humanization of non-human antibodies is complementary determining regions (CDR) grafting in which the CDRs of non-human antibodies are grafted onto the human frameworks. Usually, human frameworks with the highest homology to the framework regions of non-human antibodies are chosen as acceptors for CDR grafting.
Human germline genes could be used as an alternative source of framework regions for the humanization of murine antibodies. The germline genes have less intra-clonal somatic hypermutation. Therefore, humanized antibodies with germline frameworks show lower immunogenicity than humanized antibodies with IgG frameworks.
The antibody resurfacing method is another strategy for the humanization of non-human antibodies. This method involves replacing potentially antigenic surface framework residues with the most common human residues at those positions. Antibodies humanized by this method usually exhibit little change in stability and affinity.
Based on the most advanced techniques and years of experience in the antibody engineering field, Creative Biolabs provides the high-quality services and most reasonable experimental strategies in immune checkpoint antibody humanization. Please contact us for more detailed information to know how we can help.
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.