Antiangiogenesis therapy, also known as angiogenesis inhibitors, represents one of the effective therapeutic strategies for cancer. It inhibits the growth of tumor cells by blocking the growth of blood vessels that support tumor growth. Although angiogenesis inhibitors provide rapid disease control and high response rates, they may be limited durability as monotherapy.
Immune checkpoint therapy, also known as immune checkpoint inhibitors, targets regulatory pathways in T cells and promotes the activation of cancer-killing immune cells, enhancing anti-tumor immune responses. The combination of immune checkpoint therapy with anti-angiogenesis therapy has revolutionized the treatment of advanced cancers, which provide a synergistic anti-tumor effect.
Angiogenesis and immunosuppressive microenvironment are two very important factors for the development of tumor progression. Tumor angiogenesis is highly dependent on the immunosuppressive microenvironment, while tumor immune escape is closely related to tumor angiogenesis. For example, activated T cells produce interferon-γ (IFN-γ), which directly promote tumor vascular normalization and regression through interacting with IFN-γ receptors on tumor endothelial cells. Hence, the combination of anti-angiogenesis and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) can increase anti-tumor efficacy. Currently, most preclinical studies and clinical trials have been performed to investigate the synergistic effect of the combination therapy and acquired promising outcomes.
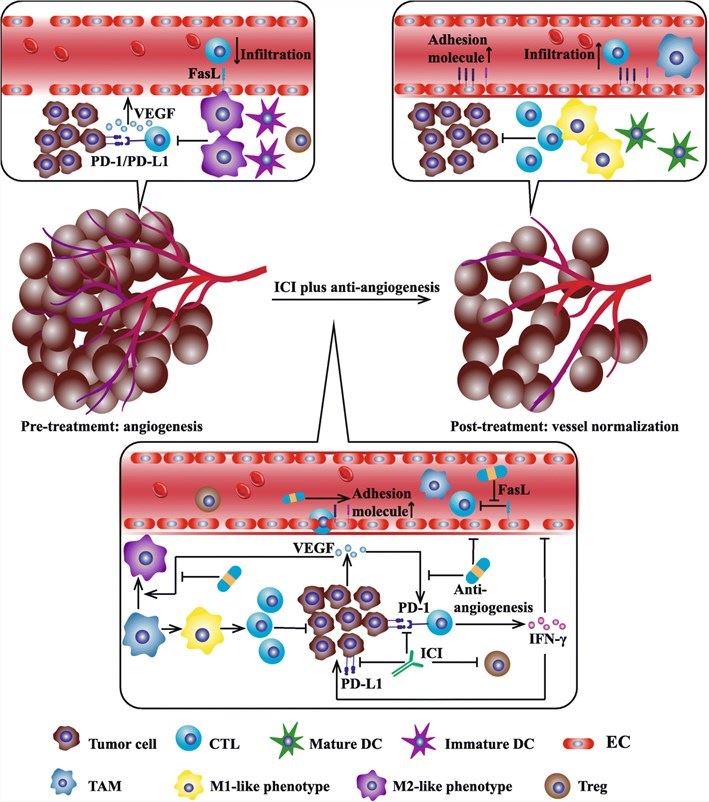 Fig.1. Mutual regulation of tumor vessel normalization and immune microenvironment reprogramming.1,2
Fig.1. Mutual regulation of tumor vessel normalization and immune microenvironment reprogramming.1,2
With the advent of ICIs and angiogenesis inhibitors, there is interest in empirically combining these two therapies with the hopes of preserving high response rates and adding durability. A number of trials have demonstrated that the combination of VEGF inhibitors with ICIs increases response rates, tumor shrinkage, and progression-free survival (PFS) compared with immunotherapy alone in advanced and metastatic RCC.
The concept of combination of ICIs and angiogenesis inhibitors is based on the immunomodulatory role of VEGF-A observed in multiple cancers. Inhibition of VEGF-A can increase the number of intratumoral CD8+ cells and impair tumor growth. Several clinical trials are being performed to evaluate the effect of combining ICIs and angiogenesis inhibitors on HCC. The study reported HCC patients treated with combination of anti-VEGF antibody and anti-PD-L1 antibody showed RECIST response rates of 34%. But approximately 25% of patients exhibited grade 3-4 toxicity, including mostly hypertension, abnormal liver tests, and autoimmune manifestations. Another early-phase study showed that treatment with combination of multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors and anti-PD-1 antibodies exhibited a radiological response rate of 46% in 13 HCC patients, with acceptable toxicity.
Creative Biolabs is a world-leading services provider who is devoted to providing a series of immune checkpoint therapy services, including but not limited to:
If you are interested in our services, please contact us to discuss your project.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.