The tumor mass is not solely comprised of a heterogeneous population of cancer cells; it also encompasses a diverse array of resident and infiltrating host cells, secreted factors, and extracellular matrix proteins, collectively referred to as the tumor microenvironment (TME). The trajectory of tumor progression is profoundly shaped by the intricate interplay between cancer cells and their environment, ultimately dictating whether the primary tumor is eliminated, spreads to distant sites through metastasis, or establishes dormant micrometastases. Moreover, the TME exerts significant influence over therapeutic responses and resistance, underscoring the recent emphasis on targeting its components, as exemplified by the notable clinical success of immune checkpoint inhibitors.
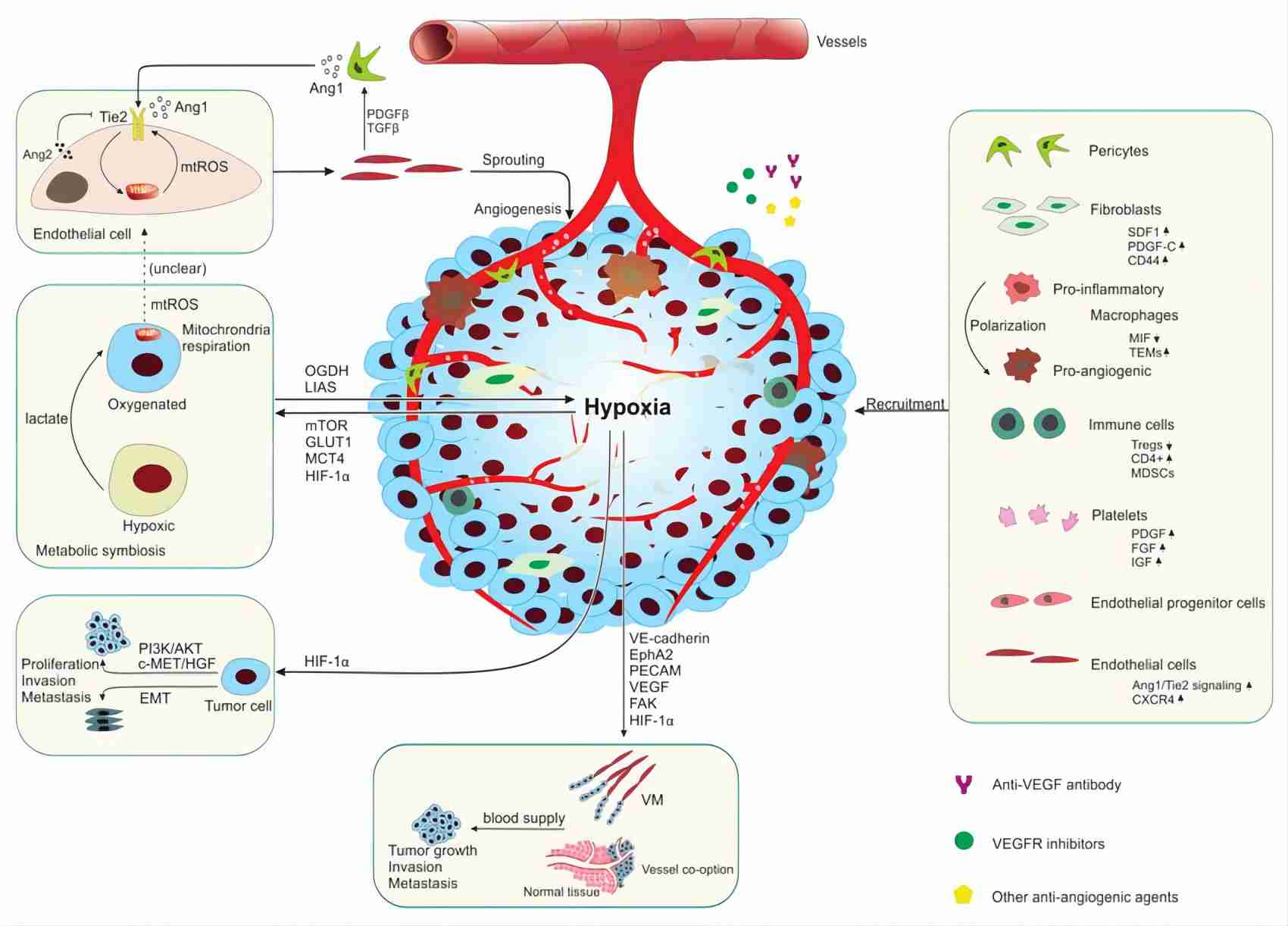 Fig.1. Unveiling the TME's impact on anti-angiogenic therapy resistance.1,4
Fig.1. Unveiling the TME's impact on anti-angiogenic therapy resistance.1,4
TME signifies a reservoir of pivotal regulators governing immune responses against cancer, encompassing both tumor cells and T-cells. Furthermore, certain regulators predominantly encompass immunosuppressive cellular elements, molecules, cytokines, and chemokines.
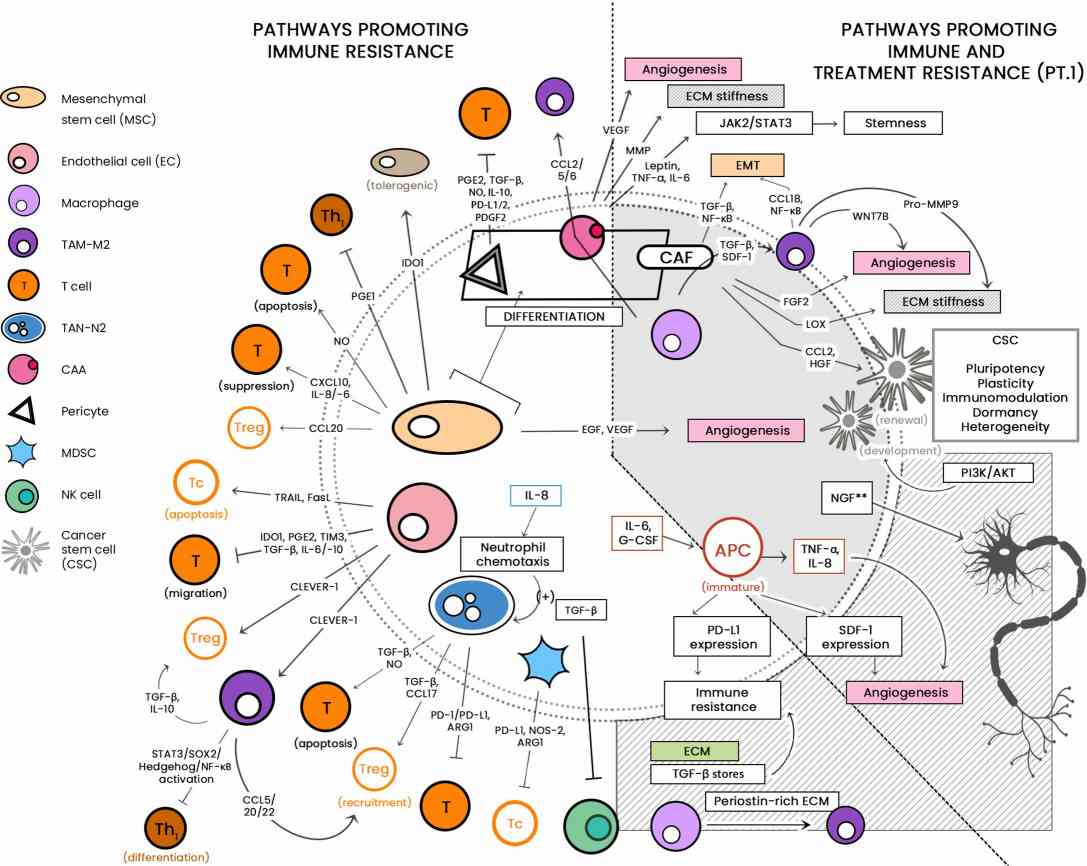 Fig.2. Illustrating the diverse cellular landscape of the TME.2,4 |
The TME, encompasses diverse elements, including its vasculature, stromal components, immune cells, and extracellular matrix, fostering an immunosuppressive and nutrient-deprived milieu essential for tumor growth, adaptation, and resistance to therapies. Cellular crosstalk and cell-to-ECM communication within the TME drive the release of soluble factors, facilitating immune evasion and ECM remodeling, further exacerbating resistance to treatment. Factors such as exosomes, deregulated microRNAs, TME-specific metabolic patterns, hypoxia, metabolic dysregulation, and mechanical forces contribute to treatment resistance, making the TME a pivotal focus in understanding and combating therapy resistance. |
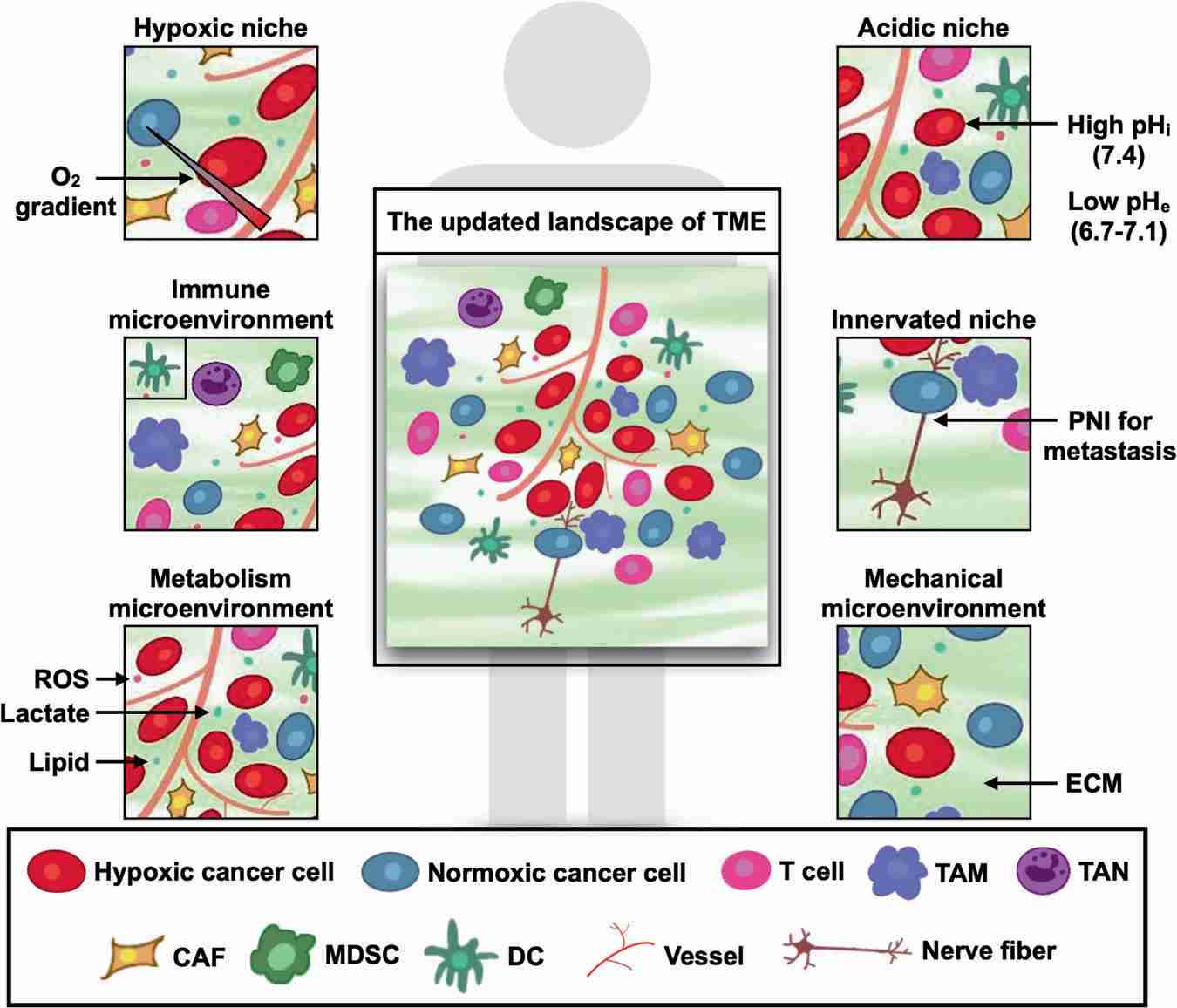 Fig.3. Revisiting the evolving terrain of the TME.3,4 |
TME has emerged as a critical factor in shaping tumor behavior and responses to therapies, shifting the focus of cancer research and treatment from the tumor itself to the TME. Despite this shift, the clinical effectiveness of TME-targeted therapies remains limited, emphasizing the need for a better understanding of TME characteristics and interactions among its components to develop more potent treatment approaches. This comprehensive review delves into various facets of the TME, including hypoxia, immune responses, metabolic influences, acidity, neural connections, and mechanical factors, while also exploring the potential repurposing of conventional drugs for innovative anti-tumor applications, offering valuable insights into the future of TME-driven cancer treatment strategies. |
Creative Biolabs offers an extensive array of customized services related to immune checkpoints, which include but are not limited to: Immune Checkpoint Antibody Development, Immune Checkpoint Assays, Immune Checkpoint Targeted Peptide Development, etc. Please contact us for a thorough understanding.
References
All listed customized services & products are for research use only, not intended for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
USA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Copyright © 2026 Creative Biolabs. All Rights Reserved.